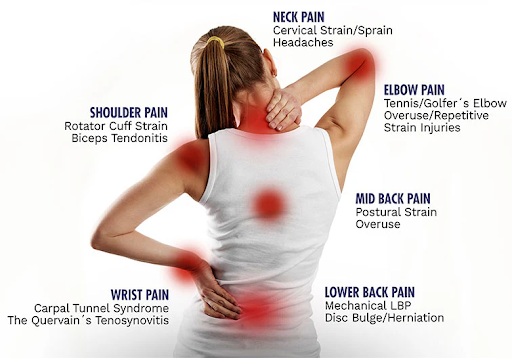
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI): A Common Workplace Complaint
Repeated Strain Injury (RSI) is a common problem among office and manual labour workers, resulting from repeated jobs, extended computer usage, and poor ergonomic standards. RSI frequently affects muscles, nerves, and tendons, particularly in the hands, wrists, elbows, and shoulders, resulting in symptoms such as discomfort, stiffness, and restricted mobility.
Statistics show that RSI is prevalent in workplaces across the world. According to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), over 500,000 UK workers experienced RSI-related symptoms in 2022, indicating a rise in occurrences owing to increased hours in digital workplaces. Similarly, the U.S. Bureau of Labour Statistics (BLS) says that musculoskeletal diseases, including RSI, account for roughly 30% of all workplace injuries, reducing productivity and increasing healthcare expenditures.
Ergonomic workspace changes, regular breaks, and appropriate posture awareness are all important preventative strategies. Companies that use RSI preventive techniques have reported higher productivity and fewer injury-related expenditures. Employers might benefit from frequent training and workstation evaluations to ensure employee well-being.
References:
- Health and Safety Executive (HSE). “Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Statistics in Great Britain, 2022.”
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). “Nonfatal Occupational Injuries and Illnesses Requiring Days Away from Work, 2021.”
Embrace mindfulness and meditation during pregnancy to boost relaxation, reduce stress, and support emotional well-being. Learn techniques designed to help you stay centered and calm throughout your pregnancy journey.
Embrace mindfulness and meditation during pregnancy to boost relaxation, reduce stress, and support emotional well-being. Learn techniques designed to help you stay centered and calm throughout your pregnancy journey.



